Have you ever wondered why certain plants thrive in your neighbor's garden but struggle in yours? The secret lies in understanding USDA Agriculture Zones, a valuable tool that can make or break your gardening success. In this post, let's delve into the importance of USDA Agriculture Zones and how they guide us towards creating thriving, climate-appropriate gardens.
What are USDA Agriculture Zones?
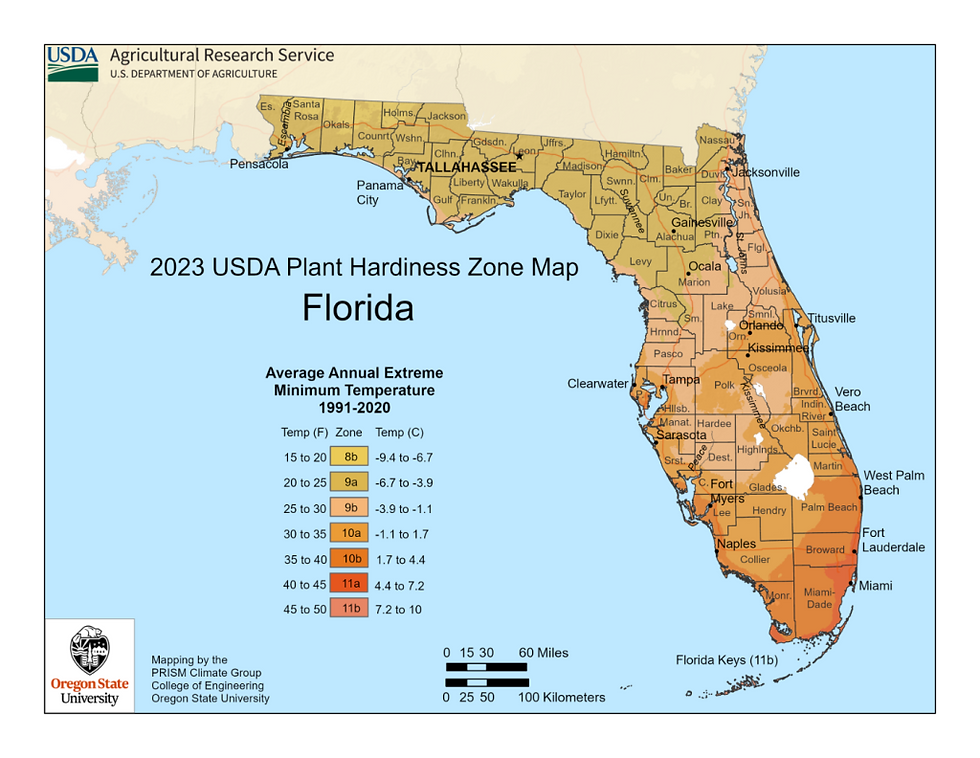
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides the United States into different zones based on average annual minimum winter temperatures. Each zone represents a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference, providing a comprehensive overview of the climate in various regions. The higher the zone number, the warmer the average winter temperatures in that area.
*It is important to note that the USDA zones have recently been updated with changes. See the graphic below for the most updated zone information.
Why are USDA Agriculture Zones Crucial for Gardening Success?
Plant Suitability: Different plants have specific temperature requirements for optimal growth. Understanding your USDA Zone helps you choose plants that are well-suited to your local climate. For example, a plant that thrives in Zone 8 might struggle in Zone 4 due to colder temperatures.
Frost Dates: USDA Zones play a crucial role in determining the average dates of the first and last frost in your area. Knowing these dates is essential for planning your gardening calendar. Planting too early or too late can have a significant impact on your garden's success.
Plant Hardiness: The Zone Map also indicates the plant hardiness of different species. This information is valuable in selecting plants that can withstand the winter temperatures in your region. Plants labeled as "hardy to Zone X" are likely to thrive in that specific zone and lower.
Microclimates: While USDA Zones provide a general guideline, it's essential to recognize that microclimates exist within larger zones. Factors such as elevation, proximity to bodies of water, and urban heat islands can influence local temperatures. Observing your specific microclimate helps you fine-tune your plant selections.
Pest and Disease Management: Climate significantly affects the prevalence of pests and diseases. By aligning your plant choices with your USDA Zone, you reduce the risk of introducing plants that may be susceptible to local pests. This promotes a healthier and more resilient garden ecosystem.
How to Determine Your USDA Agriculture Zone:
Discovering your USDA Zone is a straightforward process. Visit the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map online or consult with your local gardening center. Simply input your ZIP code, and you'll be provided with valuable information about your zone, including average annual minimum temperatures.
Conclusion:
In the intricate world of gardening, knowledge is power, and understanding your USDA Agriculture Zone is like having a secret weapon for success. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or just starting, aligning your plant choices with your local climate ensures a flourishing and resilient garden. So, fellow garden enthusiasts, share your USDA Zone and experiences, and let's create thriving gardens tailored to the unique climates we call home!
_edited.png)




